Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- programmers
- 가상환경
- 프로그래머스
- Join
- openCV
- pandas
- 백준
- Stack
- dataframe
- python
- Algorithm
- Matplotlib
- 알고리즘 스터디
- 정보처리기사 c언어
- 자료구조
- MySQL
- String Method
- type hint
- 선그래프
- 코딩테스트
- 노마드코딩
- 알고리즘스터디
- NumPy
- queue
- aws jupyter notebook
- 파이썬
- 알고리즘
- Selenium
- 데이터시각화
- javascript
Archives
- Today
- Total
조금씩 꾸준히 완성을 향해
[C 언어] 함수 주소 전달 & 주소 리턴 본문
<예제 1>
#include <stdio.h>
int f(int *i, int j);
int main(void){
int x=10, y=20;
printf("%d\n", f(&x, y));
printf("%d %d", x, y);
}
int f(int *i, int j){
*i += 5;
return (2* *i + ++j);
}
// 51
// 15 20
<예제 2>
#include <stdio.h>
int foo(int a, int *b);
int main(){
int a=5;
int b=3;
int c=0;
b = foo(a, &c);
c = foo(b, &c);
printf("a=%d b=%d c=%d", a, b, c);
}
int foo(int a, int *b){
int c;
*b = a+1;
c = a-1;
return c;
}
// a=5 b=4 c=3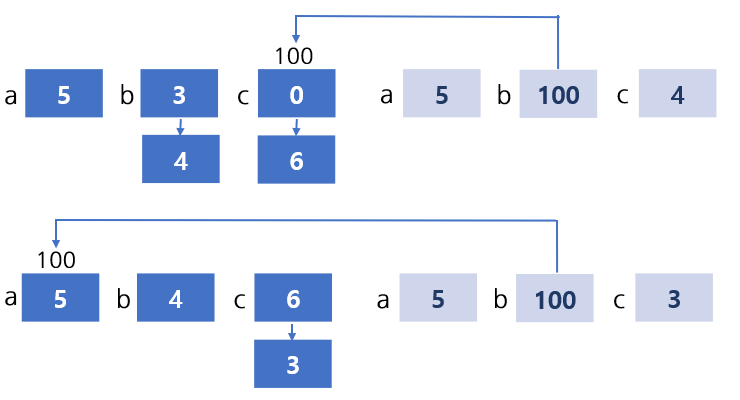
<예제 3>
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int a, int *b);
int main(){
int value=3, list[4]={1,3,5,7};
int i;
swap(value, &list[0]);
swap(list[2], &list[3]);
swap(value, &list[value]);
for(i=0; i < 4; i++)
printf("%d",list[i]);
}
void swap(int a, int *b){
int temp;
temp = a;
a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
//3353
<예제 4>
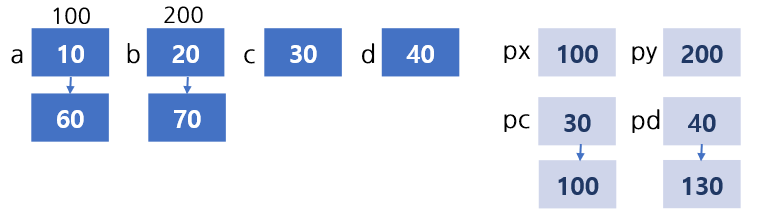
#include <stdio.h>
void change(int *px, int *py, int pc, int pd);
int main(void) {
int a=10, b=20, c=30, d=40;
change(&a, &b, c, d);
printf("a=%d, b=%d, c=%d, d=%d", a, b, c, d);
}
void change(int *px, int *py, int pc, int pd){
*px = *py + pd;
*py = pc + pd;
pc = *px + pd;
pd = *px + *py;
}
// a=60, b=70, c=30, d=40
<예제 5>
#include <stdio.h>
double h(double *f, int d, double x);
int main(void) {
double f[] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
printf("%3.1f", h(f, 4, 2));
return 0;
}
double h(double *f, int d, double x){
int i;
double res = 0.0;
for(i=d-1; i>=0; i--){
res = res * x + f[i];
}
return res;
}
// 49.0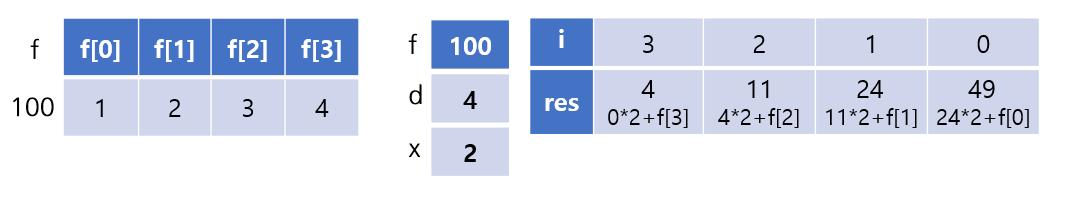
<예제 6>
#include <stdio.h>
void func(int *a, int b, int *c);
int main() {
int a, b, c[1];
a=20;
b=20;
c[0] = 20;
func(&a, b, c);
printf("d=%d, b=%d, c=%d", a, b, c[0]);
return 0;
}
void func(int *a, int b, int *c){
int x;
x = *a;
*a = x++;
x = b;
b = ++x;
--(*c);
}
// a=20, b=20, c=19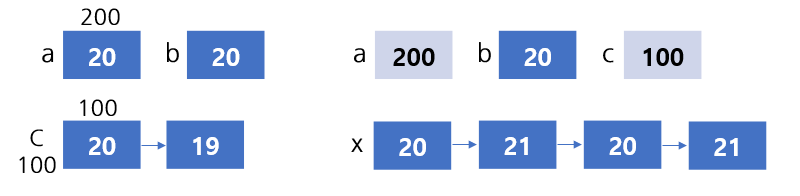
<예제 7>
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 3
void func(int *m, int *x, int y);
int main() {
int num[SIZE] = {1, 3, 6};
int a=10, b=30;
func(num, &a, b);
printf("a=%d, b=%d", a, b);
return 0;
}
void func(int *m, int *x, int y){
int i=0, n=0;
y = *x;
n = *(m+1) + (*m+2);
*x = ++n;
}
// a=7, b=30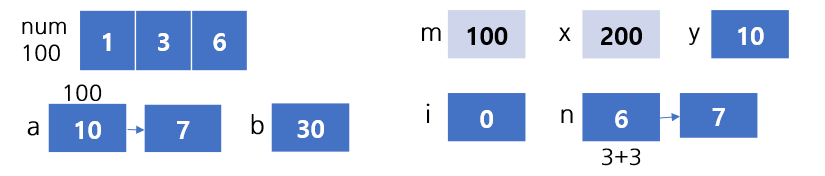
<예제 8>
#include <stdio.h>
int *func(int a, int *x);
int main() {
int i;
int x=10;
int *p;
int a[100];
for(i=0; i<100; i++)
a[i] = i*10;
p = func(x, a);
printf("sum=%d", x + a[0] + a[1] + p[0] + p[1]);
}
int *func(int a, int *x){
a = a + 10;
x = x + 1;
*x = *x * 2;
return x;
}
// sum=70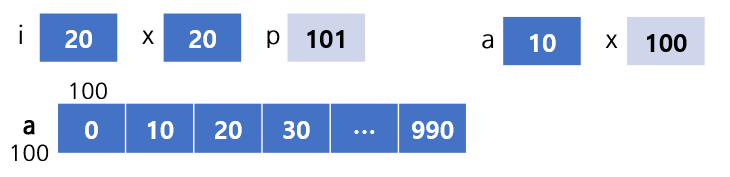
※ 유튜브 흥달쌤 깨알 C언어 특강을 직접 정리한 내용입니다
'기타 언어 > C 언어' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C 언어] 재귀 함수 (0) | 2023.03.29 |
|---|---|
| [C 언어] 정적(STATIC) 변수 (0) | 2023.03.29 |
| [C 언어] 함수 (0) | 2023.03.22 |
| [C 언어] 배열 포인터 (0) | 2023.03.22 |
| [C 언어] 구조체(struct) (0) | 2023.03.22 |



