Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 알고리즘
- Matplotlib
- openCV
- 가상환경
- Algorithm
- 파이썬
- 노마드코딩
- String Method
- pandas
- 알고리즘 스터디
- 자료구조
- 프로그래머스
- aws jupyter notebook
- programmers
- 정보처리기사 c언어
- 데이터시각화
- 백준
- 선그래프
- 알고리즘스터디
- Stack
- javascript
- Join
- MySQL
- NumPy
- Selenium
- dataframe
- python
- queue
- 코딩테스트
- type hint
Archives
- Today
- Total
조금씩 꾸준히 완성을 향해
[자료 구조] Python 해시테이블(Hash Table)의 활용(Dictionary 반복문, 정렬 등) 본문
DataStructure & Algorithm/이론 정리
[자료 구조] Python 해시테이블(Hash Table)의 활용(Dictionary 반복문, 정렬 등)
all_sound 2022. 10. 10. 21:13해시 테이블 (Hash Table)
- Hash Table? 키(Key)에 데이터(Value)를 저장하는 데이터 구조
- Key를 통해 데이터를 바로 받아올 수 있음 → 속도가 획기적으로 빨라짐
- 파이썬 딕셔너리(Dictionary) 타입이 해쉬 테이블의 예 - Key를 가지고 바로 데이터(Value)를 꺼냄
- 보통 배열로 미리 Hash Table 사이즈만큼 생성 후 사용(공간과 탐색 시간을 맞바꾸는 기법)
- 파이썬에서는 해쉬를 별도로 구현할 필요 없음 - 딕셔너리 타입을 사용하면 되기 때문
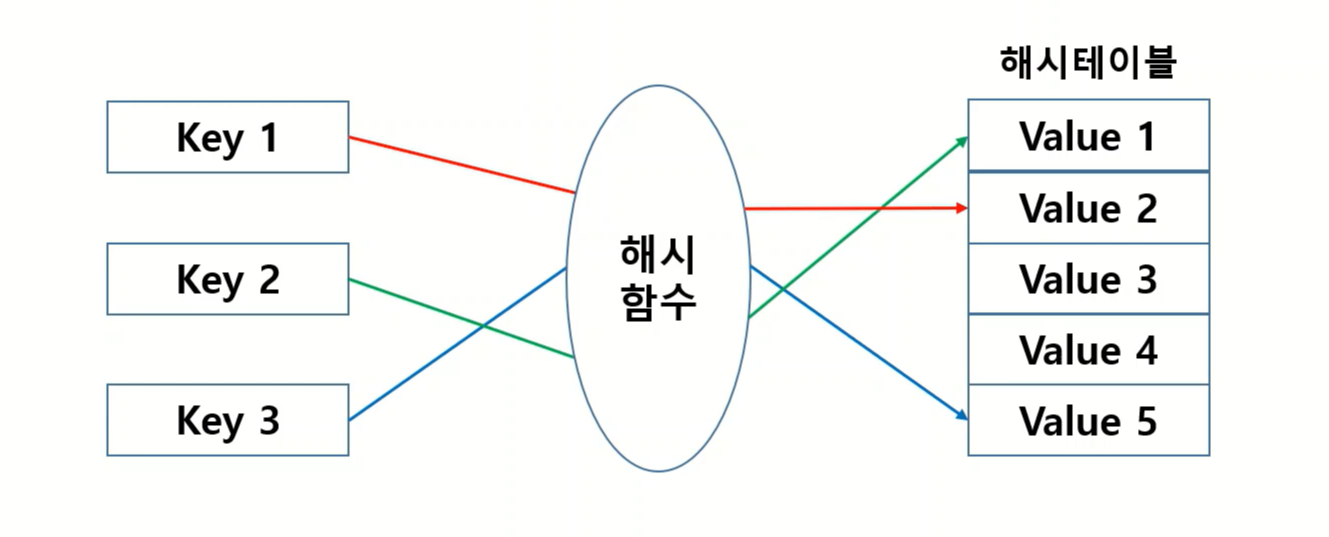
해시 함수란?
임의의 길이를 갖는 메세지를 입력받아 고정된 길이의 해시값을 출력하는 함수

Python Hash (Dictionary) 의 활용
▶ 딕셔너리 삽입
hash = dict() hash = {} #딕셔너리 생성
hash[1] = 'apple' #int : str
hash['banana'] = 3 #str : int
hash[(4,5)] = [1,2,3] #tuple : list
hash[10] = dict({1:'a', 2: 'b'}) #int : dict
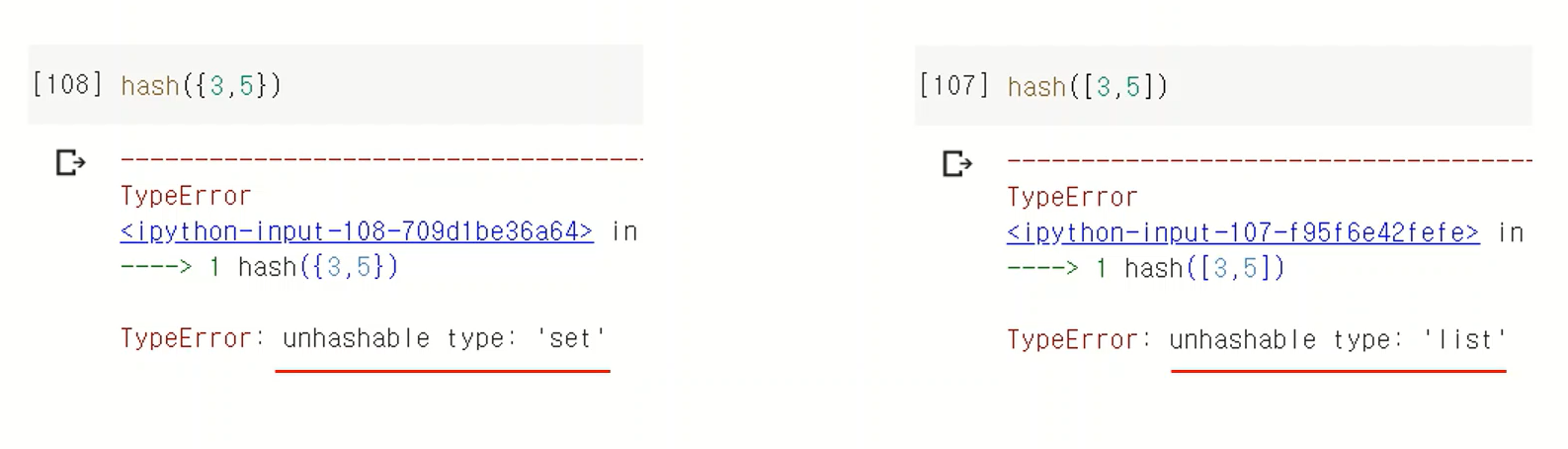
※ 주의! 해시 불가능 타입
- set 과 list는 불가능
- hash 함수에 의해 index로 변환이 불가능
▶ 딕셔너리 수정
hash[1] = 'melon'
hash['banana'] = 10
▶ 딕셔너리 값 추출
hash.pop(1) # melon
hash.pop('banana') # 10
hash.pop((4,5)) # [1,2,3]
hash.pop(10) # dict({1:'a', 2: 'b'})
▶ 딕셔너리 삭제

▶ 딕셔너리 루프

- key 추출
for k in hash.keys():
print(k)
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4
# 5
- value 추출
for v in hash.values():
print(v)
# 1
# 4
# 9
# 16
# 25
- key와 value 추출
for k, v in hash.items():
print(k, v)
# 1 1
# 2 4
# 3 9
# 4 16
# 5 25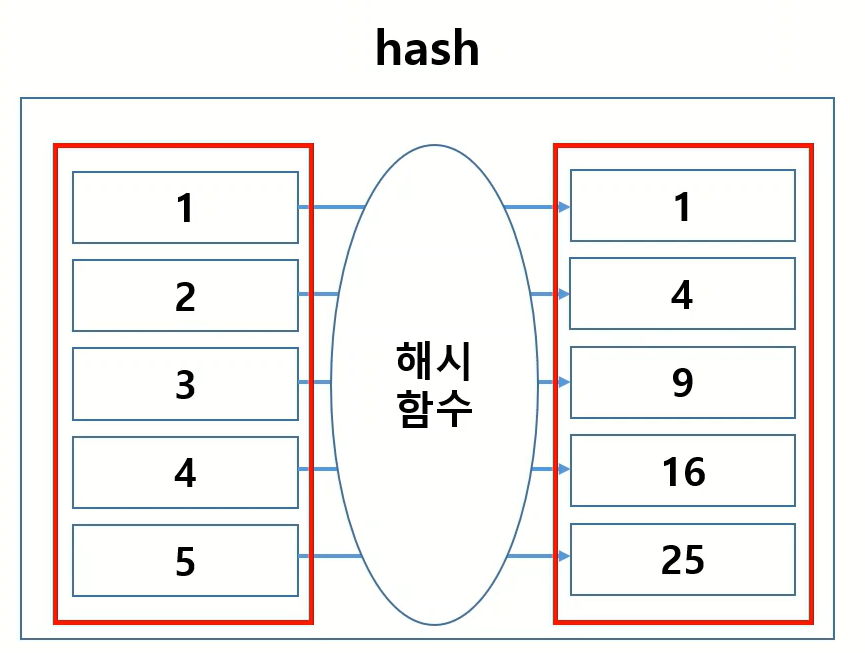
▶ 딕셔너리 정렬
sorted() 함수 사용 (※주의! 항상 list 타입을 반환)
- 오름차순 정렬
hash = dict({1: 10, 3: 12, 5: 7, 7 : 6, 4: 5})
# Keys
sorted(hash.keys(), key = lambda x : x)
# [1,3,4,5,7]
# Values
sorted(hash.values(), key = lambda x : x)
# [5,6,7,10,12]
# Keys Values
sorted(hash.items(), key = lambda x : x)
# [(1, 10), (3, 12), (4, 5), (5, 7), (7, 6)]
- 내림차순 정렬
hash = dict({1: 10, 3: 12, 5: 7, 7 : 6, 4: 5})
# Keys
sorted(hash.keys(), key = lambda x : -x)
# [1,3,4,5,7]
# Values
sorted(hash.values(), key = lambda x : -x)
# [5,6,7,10,12]
- key와 value 값에 의한 내림차순
※ 주의! items()는 튜플 형태(key, value)이기 때문에 key = lambda x : -x 불가능!!
# Value에 의한 내림차순
sorted(hash.items(), key = lambda x : -x[1])
# [(3, 12), (1, 10), (5, 7), (7, 6), (4, 5)]
# Keys Values 다양한 정렬 조합
# key 오름차순, value 오름차순
sorted(hash.items(), key = lambda x : (x[0], x[1]))
# key 내림차순, value 오름차순
sorted(hash.items(), key = lambda x : (-x[0], x[1]))
# value 오름차순, key 오름차순
sorted(hash.items(), key = lambda x : (x[1], x[0]))'DataStructure & Algorithm > 이론 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료 구조] 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)와 힙(Heap) (0) | 2022.10.10 |
|---|---|
| 그리디 알고리즘(탐욕법) / Greedy Algorithm (0) | 2022.10.10 |
| Python 알고리즘의 성능 평가 (1) | 2022.10.10 |
| [자료 구조] Queue (0) | 2022.10.03 |
| [자료 구조] Stack (0) | 2022.10.02 |



